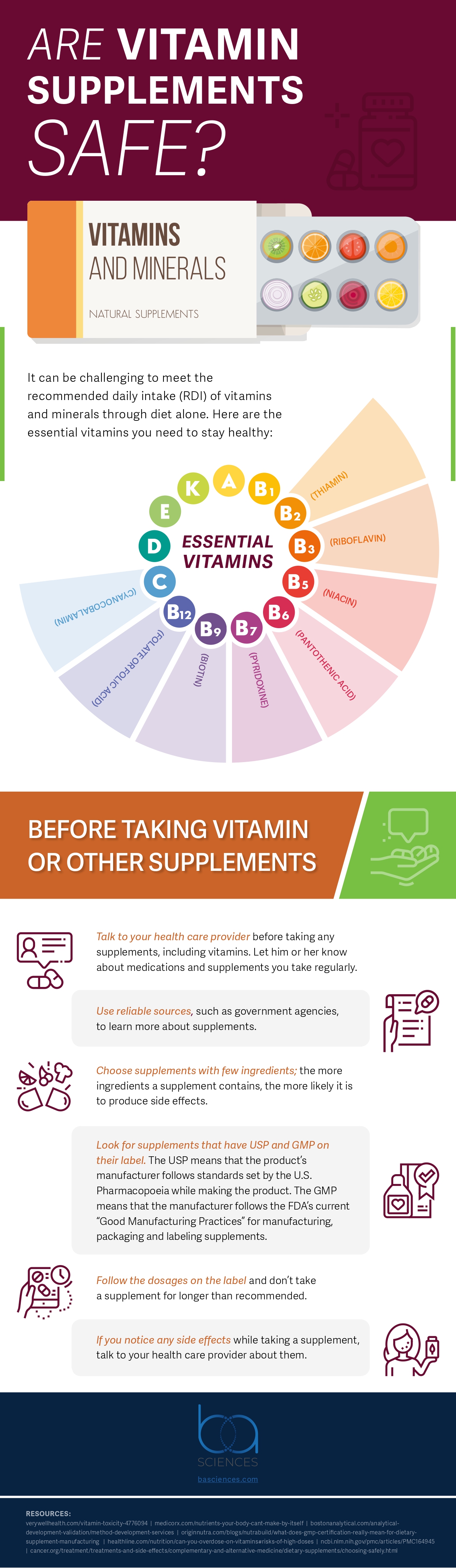
Meeting the daily recommended intake of vitamins and minerals through diet alone can be challenging, prompting many people to use supplements. In fact, 58% of adults take a multivitamin, and about 75% of Americans use dietary supplements. However, it’s important to be aware of the risk of vitamin overdose.
Vitamins fall into two categories: fat-soluble and water-soluble. Water-soluble vitamins are utilized by the body as needed and any excess is typically expelled, reducing the risk of toxicity. On the other hand, fat-soluble vitamins — specifically A, D, E, and K — are stored in fat and the liver, which can lead to toxicity if taken in large amounts.
Before beginning or altering any supplement routine, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure the dosages are safe and beneficial. The infographic “Are Vitamin Supplements Safe?” offers a comprehensive overview of the cautious use of vitamin supplements.
Infographic created by BA Sciences, offering a wide array of pharmaceutical analytical testing services